Abstract
Introduction: Autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT) are standard of care for patients with primary refractory or recurrent Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). While transplant results in cure for some patients, others relapse and succumb from their disease. Studies have found high expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in HL cells. The anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, nivolumab, has been safe and efficacious in the treatment of relapsed, refractory HL (Ansell et al. 2015). We evaluated the safety and efficacy of nivolumab maintenance therapy post-ASCT in high risk for relapse Hodgkin disease.
Methods: Patients with HL with high risk of residual disease following ASCT ( high risk defined as refractory disease, relapse <12 months, or relapse ≥12 months with extranodal disease after frontline therapy) received nivolumab (240 mg IV every 2 weeks) starting 45-180 days post-transplant for a maximum of 6 months of treatment. Patients were followed for AEs through 100 days after the last dose of drug. PET-CT response assessments were performed 1-3 month, 6 month, and 12 month post-ASCT. The primary objective was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of nivolumab as maintenance therapy early after ASCT. The secondary objective was to evaluate progression-free survival (PFS) at 12 months post-transplant.
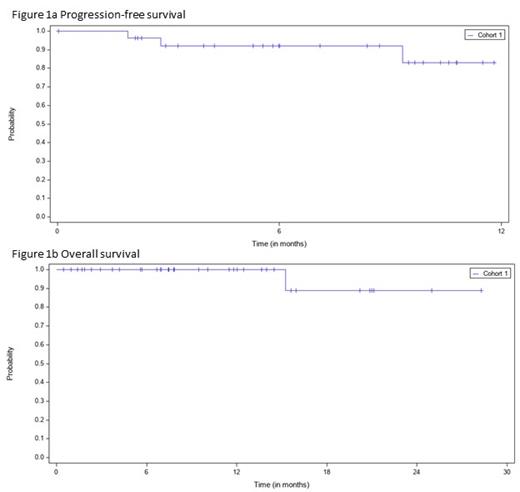
Results: To date, 37 patients were enrolled; median age 36 years; 25 patients (68%) male. The median number of prior systemic regimens was 2 (range 2-4). 25 patients (68%) had relapsed disease, and 12 patients (32%) had primary refractory disease. 18 patients (49%) had extranodal disease at relapse, 6 patients (16%) had B-symptoms at relapse, and 11 patients (30%) had residual disease after salvage, including 10 patients (27%) of whom had 2-3 prior salvage therapies. 22 patients (60%) had received prior brentuximab, and 3 patients (8%) had received prior nivolumab or pembrolizumab. 36 patients received ASCT and 1 patient received tandem ASCT. At the time of data cutoff, 28 patients (76%) had discontinued nivolumab treatment, 22 patients (60%) because they had completed the 6-month treatment course, 4 patients (11%) due to an adverse event (AE) (1 patient each with pain, pneumonitis, rhabdomyolysis, or hypothyroidism), and 2 patients (5%) due to disease progression. The median duration of treatment was 22.1 weeks. 17 patients (46%) experienced a treatment-related AE (TRAE), of which 5 patients (14%) experienced a ≥Grade 3 TRAE. The most common (≥5%) TRAEs were diarrhea, fatigue, bone pain, neutrophil count decreased, pruritus, rash, and vomiting. 2 patients experienced a treatment-related serious AE (pneumonitis, rhabdomyolysis). There were no treatment-related deaths. With a median follow up of 9.2 months, the median PFS and overall survival (OS) have not been reached. The 6 month PFS is 92.1% and the 12-month OS is 100%. There were no differences in OS when stratified based on prior treatment.
Conclusions: The use of nivolumab maintenance early after ASCT is safe and tolerable in this high risk patient population. Early efficacy data is promising, but data need to mature to determine the 12 month PFS.
Bachier: CRISPR: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Autolus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Nkarta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mana: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Shah: Umoja: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Legend: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; Miltenyi Biotec: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Lily: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Epizyme: Consultancy.